|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

The article below (from "A Symposium on Creation" Vols. 1-5 @ http://www.creationism.org/english/symposium/) is used by permission of Baker Books, a division of Baker Book House Company, copyright ©1968-1975. All rights to these materials are reserved. Materials are not be be distributed to other web locations for retrieval, published in other media, or mirrored at other sites without written permission from Baker Book House Company.
The Pre-flood Greenhouse Effect
(The Antediluvian Canopy)
by Donald W. Patten
From: "A Symposium on Creation"
(Vol. II), pg 11-44
©1970 - Baker
Book House
Donald W. Patten may be called both a businessman and a scholar. A Montanan by birth and a geographer by training and lifelong interest, he began reading the Bible while in college, taking courses including evolution. As a student in college, he experienced conversion to the Christian faith. Shortly thereafter, he was given pulpit duties in a small, rural, community church in the village of Lolo, Montana. He received a B.A. in geography from the University of Washington in 1951, and a M.A., also in geography, in 1962. He is the owner of a microfilming business in Seattle, and is also the founder of the Pacific Meridian Publishing Company. His publications include
What was the atmosphere of the earth like, and what was the climate of the earth like in the era before the flood? There is evidence that climates have changed dramatically, permanently and suddenly. In Arctic regions there is evidence of former luxuriant sub-tropical forests, and even huge fossil palm leaves within 800 miles of the North Pole. About 200 miles from the South Pole, where temperatures are so cold that today life cannot flourish, Admiral Byrd found fossil evidence of a once luxuriant forest.
Or in the remote cold reaches of the Northern Hemisphere, on the island of Spitzbergen, north of northern Norway, it is sufficiently cold today that ice breakers have trouble approaching even during the few weeks of late summer. Here on Spitzbergen (Svalbard in Norwegian) fossils of marine crustaceans are found which could only have lived in tropical waters. We suspect that not only have climates changed with drama, permanence and suddenness, but so also have ocean temperatures changed remarkably, if not quite so suddenly.
We have ample indication that many of the animals which lived in the pre-flood, primordial period were large -generally much larger than present animal counterparts. There were lizards, for instance, which weighed 40 tons (the brontosaurus dinosaur). There were sloths which weighed 10,000 pounds. There were insects such as butterflies with 20-inch wing spans. (What must mosquitoes have been like in this primordial era?)
Again, there were some birds with 25- and 30-foot wing spans, which laid eggs 11 inches in diameter – two gallon eggs. Recently a condor with an 18-foot wing span was unearthed, again suggesting an era in which relatively large animals were common, and gigantism among animals was normal. Interestingly enough, fossil impressions of human footprints, some measuring 20 and 22 inches from toe to heel have also been unearthed.1,2 The Scriptures, too, suggest that "there were giants in the earth in those days" (Genesis 6:4).
There are traditions from many ancient sources which suggest that man lived longer in a former era. Genesis teaches us that man lived about nine centuries, a far cry from the current threescore and ten years. Traditions of the Snohomish Indians, of the Pacific Northwest, recount that long-ago era in the misty haze of antiquity, when the sky hung low and there was no thunder or lightning, Why did the "sky hang low"? Does this suggest that at one time a different atmospheric organization, a different climatological regime existed, providing a more favorable environment for life?
Before examining details further, definitions of two terms are necessary. The term GREENHOUSE EFFECT is used to describe the totality of the earth's atmospheric envelope which apparently prevailed in the pre-flood era. This includes the lower atmosphere (the troposphere) as well as the middle and high atmospheres, the stratosphere, and the ionosphere. This, THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT, included all the mixes of gases throughout the earth's three-tiered atmosphere.
The term ANTEDILUVIAN CANOPY is used to describe only the permanent cloud cover in the lower atmosphere (the troposphere), a cloud cover which may either be described or alluded to in the following Scriptures:
And God said, Let there be a firmament [atmosphere] in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters. And God made the firmament, and divided the waters which were under the firmament [the oceans] from the waters which were above the firmament [the canopy] and it was so (Genesis l:6-7).
When I made the cloud [the canopy] the garment thereof [for the earth], and thick darkness a swaddlingband for it (Job 38:9).
"Thou coveredst it with the deep as with a garment: the waters [the canopy] stood above the mountains" (Psalm 104:6).
The permanent cloud cover of the earth, in the model which follows (to the best of our judgment and understanding), may have been 3,000 to 5,000 feet thick, and ranged between 5,000 and 10,000 feet above the earth's sea level.
A study of the earth's atmosphere and its likely ancient Greenhouse Effect can be better understood by looking briefly at the atmospheres of some of the other nearer plants. Two of the planets have no canopies. They are Mercury and Mars. Mercury has no atmosphere because of its small size and mass. Its gravity cannot overcome the kinetic energy of gaseous molecules, and they escape.
In the case of Mars, it does have a rather thin atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. There seem to be cloud formations in the atmosphere of this cold planet, particularly (a) in the polar areas in the summer, and (b) in the sunset regions of the lower latitudes. There also seem to be dust storms of high velocity. Since extreme temperature inequities create rapid wind systems, these Martian winds are not surprising. But there is no general cloud cover, and relatively little free water vapor on this barren, frozen planet.
Jupiter and Saturn do not have genuine examples of canopies because a canopy implies that sunlight can penetrate through the layer of gas. Upper atmospheric temperatures of Jupiter are around -200° F., which is much too cold for water vapor to be present. It is not too cold for ammonia and methane gases, however. These two gases are abundant in the spectra of both Jupiter and Saturn. There is also good reason to suspect, based on density ratios, that each of these planets has a deep layer of atmosphere, primarily hydrogen, over 10,000 miles thick. Neither the weak sunlight of the distant sun, 500,000,000 miles from Jupiter's orbit, nor even the intense sunlight in Mercury's region, just 28,000,000 miles from the sun, could penetrate such a thick blanket. With atmospheric pressures over 10,000 miles deep, where these Jovian planets do finally have something approaching a core, temperatures are very hot indeed.
One of Saturn's satellites is interesting. It is Titan, a satellite that is larger than either Pluto or Mercury. Titan is massive enough to retain an atmosphere, and methane bands have been recognized in its spectrum.
Venus, of course, is the most interesting planet, for it is our closest neighbor, and it possesses a very brilliant, reflective surface (called an albedo), with a reflecting power of 76 percent. This may be compared to our earth's albedo of 39 percent, with its partial cloud cover and its reflective oceans, or it may be compared to our barren non-atmospheric moon with an albedo of 7 percent. Venus has a rather dense atmosphere, comprised primarily of carbon dioxide. There is also evidence of some water vapor in its lower atmosphere. In the upper, or outer, atmosphere of Venus the intense action of solar ultra-violet radiation upon the abundant carbon dioxide has produced a high level zone, or canopy, of carbon suboxide, C3O2.
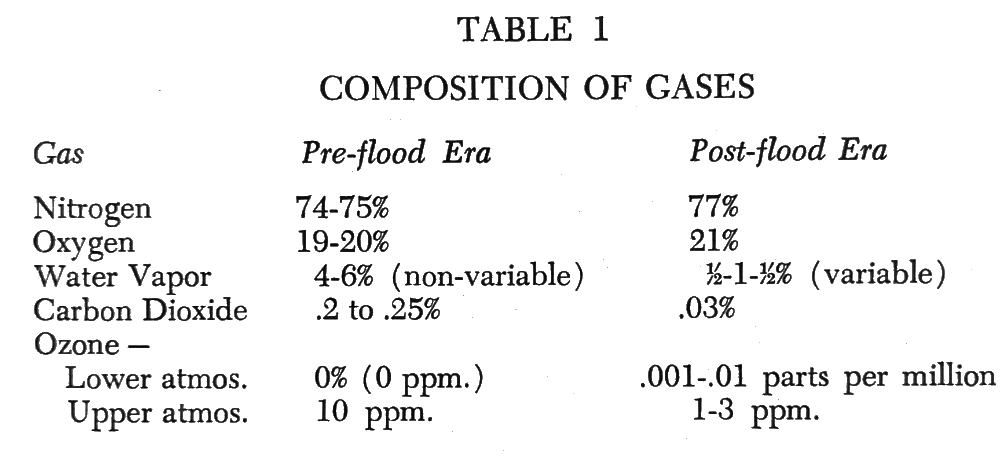
Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4 illustrate our model of the earth's pre-flood Greenhouse Effect. Figure 1 gives prime attention to temperature gradients. The pre-flood atmosphere was comprised, we suspect, of 3 to 5 times as much water vapor as is today's atmosphere. And, like today, this was concentrated in the lower troposphere.
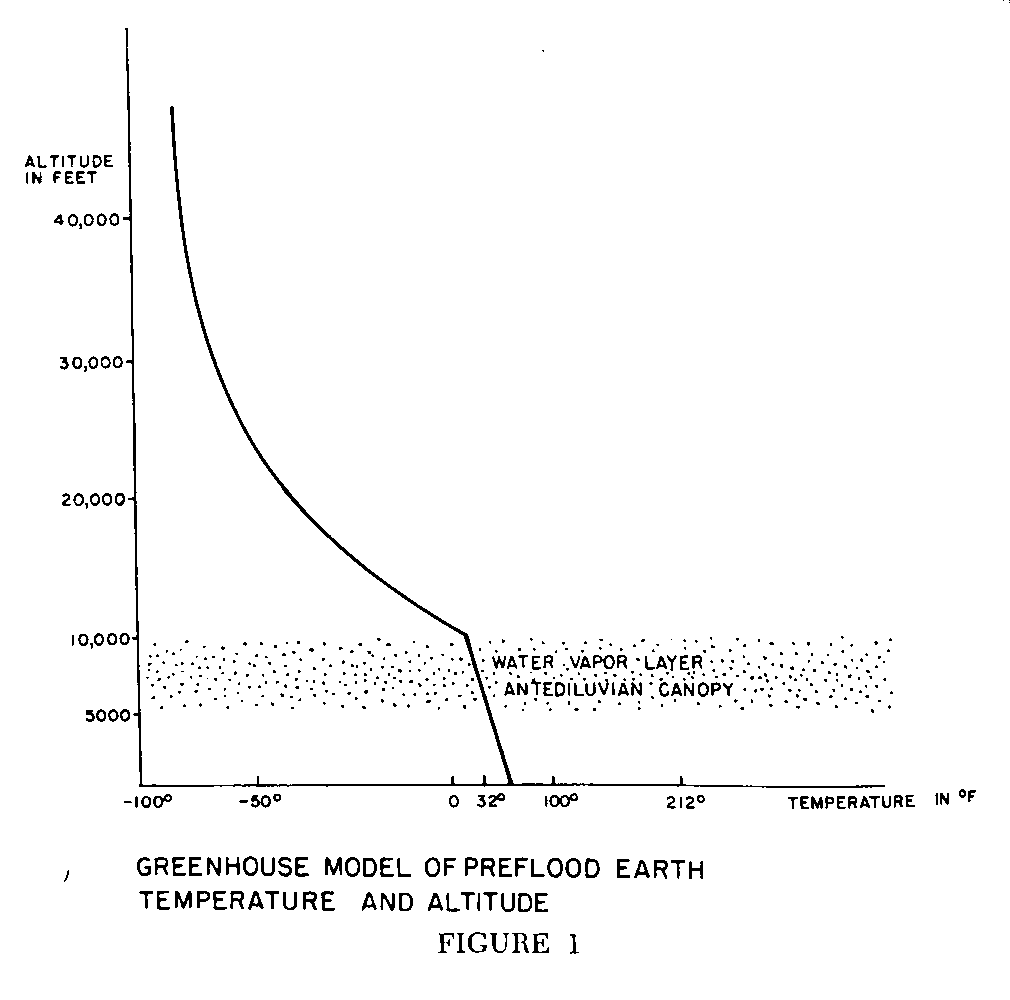
The pre-flood atmosphere is also suspected to have contained from 6 to 8 times as much carbon dioxide as the present atmosphere, which is 0.03 percent CO2, diffused in equal proportions throughout the atmosphere. The pre-flood atmosphere is suspected to have contained from 0.20 to 0.25 percent CO2, and very possibly more. Both carbon dioxide and water vapor are efficient at capturing long wave radiation, which happens to be the kind our planet's crust gives off. Hence, in the lower atmosphere, pre-flood conditions existed in which the earth lost very little of its long wave radiation, its heat. Indeed, it retained almost all.
The temperatures of the earth's surface, it is suspected, were warm on a pole-to-pole basis, and the oceans were similarly warm in high latitudes as well as in low latitudes. The daily temperature range (the diurnal range) may have been only 2° to 4° F. It was a well-insulated earth in those days, and a well-shielded earth.
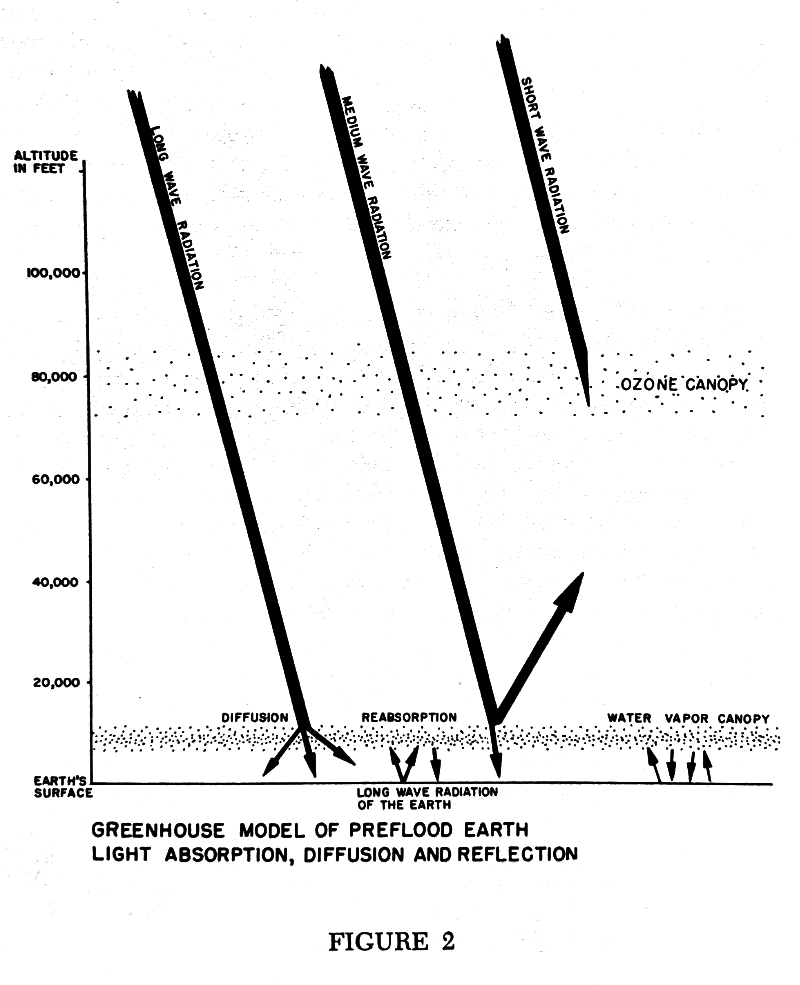
Figure 2 is an illustration to show how the earth was lighted by diffused rather than direct light. The earth's reflectivity or albedo at that time may have rivaled that of Venus (76%). Short wave radiation was filtered out through the upper level ozone layer, or ozone canopy, in the ionosphere. (Ozone concentrated in a few parts per million in the upper atmosphere becomes an effective filter for ultraviolet radiation.) Long wave radiation penetrated through the outer ozone canopy and through the intermediary stratosphere. It was partly reflected off, but primarily entered and was diffused through the water vapor canopy in the lower troposphere. The sun's long wave radiation was absorbed; and the earth's long wave radiation was captured, and its heat retained by (and within) the lower canopy.
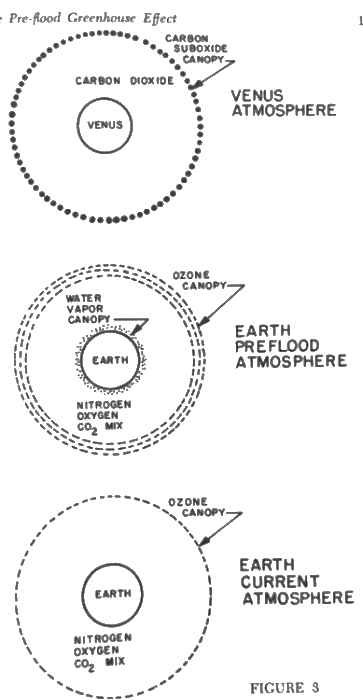
Figure 3 illustrates Venus, the present Earth, and the pre-flood Earth in terms of the outer canopy and the inner canopy. The outer canopy is ozone for the Earth, carbon suboxide for Venus. Today the earth has a dilute, or thin but most significant, outer canopy of ozone. Before the flood the ozone canopy was thicker, since ozone is (a) created by short wave solar radiation, and is (b) decomposed by long wave earth or solar radiation. The long wave earth radiation which today plays an important part in reducing the ozone canopy played no such part in the pre-flood era, since the long wave radiation was trapped in the lower atmosphere by the water vapor canopy and the stronger carbon dioxide mix.
Hence, in the pre-flood era the earth had a double canopy, where-as today it has only a dilute, high level single canopy. In the pre-flood era the earth had (a) a thicker and more efficient high level ozone canopy, (b) a thick and efficient low level water vapor canopy, and (c) a more concentrated general mix of carbon dioxide. The inner canopy was a low, unbroken water vapor condition.
Evidence will be presented as to why the pre-flood atmosphere contained more carbon dioxide and more water vapor than does the present atmosphere. This would logically suggest that the earth's barometric pressure at sea level in the pre-flood era was higher - slightly higher than in the present era.
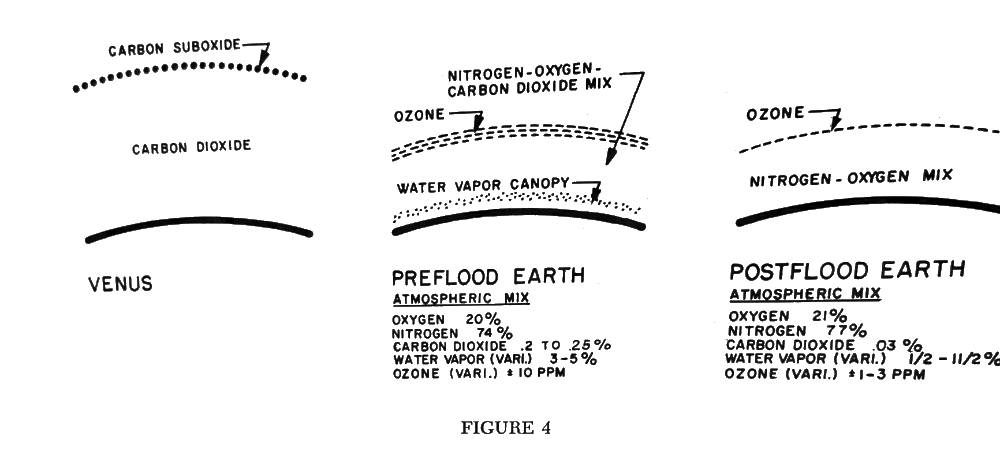
Changes in mixes of gases in the atmosphere may seem subtle, and possibly irrelevant. The atmosphere only weighs less than one-millionth of the earth's mass, but relatively light or not, here is the life zone, and here is the earth's most exposed and unstable fluid. Relatively small changes in the fluid atmosphere, upon further research, may yield an understanding as to why tropical climates prevailed in now polar regions, or why animals generally grew larger, or why men reportedly lived so long,
The existence of both a canopy, and a general greenhouse effect is suggested in the Scriptures, and is deduced from the record in the rocks. There is ample evidence that such parched regions as the Sahara Desert, the Great Australian (Sandy) Desert, the Chilean Atacama Desert, and the deserts of the American West were formerly well-watered, humid, and even swampy regions.
For instance, near Cairo one may find evidence of broad leaf forests which were suddenly entombed and petrified; Cairo today has 3 or 4 inches of rain in one of its wetter years. Again, throughout the dry, arid or semi-arid American West, in such states as Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, Nevada, and California, as well as Mexican Sonora, we find petrified forests containing broad leaf deciduous trees, coniferous trees, and even palm trees. And the rings in the trees do not suggest slow growth patterns, which dry climates would induce. Rather, the trees were large and fast growing, as was the other associated vegetation. This suggests that there has been a profound, and perhaps also a sudden change in humidity in these formerly well-watered regions.
A climate may be measured in terms of humidity. For instance, the interior of Antarctica may qualify as a desert, even though frozen water abounds. It receives about as much annual precipitation as does the Sahara Desert, but in a much different temperature range, and hence evaporation ratio. Humidity changes are one thing, and temperature changes are another. Have there also been dramatic, profound and sudden climatic changes in terms of temperature? Concerning Arctic conditions, observe:
The luxuriant growth of broad leaf hardwood forests in high Arctic latitudes persisted ... indicating a prolonged continuation of humid, warm temperature, or at least temperate forest climates in polar regions. Evidence for this may be found in both Arctic and Antarctic regions.3
The rock fragments from this mountainside invariably included plant fossils, leaf and stem impressions, coal and fossilized wood. Here at the southernmost known mountain in the world, scarcely two hundred miles from the South Pole, was found conclusive evidence that the climate of Antarctica was once temperate or even sub-tropical.4
In the Yukon Territory of Canada, so celebrated in the works of Robert Service for its harsh, long and dark winters, its icy blasts and hardy miners, sub-tropical lotus seeds have been found imbedded in frozen ground. This illustrates that the frozen Yukon once had a climate similar to Formosa, Okinawa, Kyushu or Shikoku, and possibly as tropical as the Philippine Islands.
Equally conclusive, and perhaps more dramatic is the evidence which suggests that serene, Siberian mammoths and rhinos, grazing on sub-tropical or temperate vegetation, marbled in fat, surrounded by sedges, berry bushes, and fruit trees, were suddenly plunged not merely into freezing conditions, but into conditions so cold that they were lethal to animals, clad in fur, weighing many tons. Baron Tol was credited with the discovery of at least two mammoths, in 1885 and 1886, among the now frigid islands north of Siberia.
Baron Edward Toll, the explorer, reported finding a fallen 90-foot fruit tree with ripe fruit and green leaves still on its branches, in the frozen ground of the New Siberian Islands. The only tree vegetation that grows there now is the one-inch high willow.5
Evolutionary-uniformitarian theorists have supposed that no global catastrophes have occurred; their framework does not allow for such - all changes were gradual. (The present is the the past, they presume.) Consider the problems that the uniformitarians and evolutionists have with the Beresovka mammoth, whose carcass now resides in a St. Petersburg museum. It contains the following features:
There are other problems, such as associated fruit trees with green leaves, and even ripe fruit in these regions in the permafrost. There are quick-frozen pachyderms in some regions, and apparently almost simultaneous quick-drowned pachyderms in other regions, requiring some kind of catastrophic synchronization.
Herein are presented just some bits of geological evidence that climates have changed both suddenly and dramatically, and in varying degrees of permanence, and such changes are in terms of both (a) temperature, and (b) humidity. The whole problem, of course, is more complex than merely a concern with atmospheric temperatures. As was previously noted, tropical marine crustaceans are found in high Arctic latitudes suggesting there has also been a profound drop in oceanic temperatures. A former luxuriant, moderate climate has been turned, in some areas, into parched deserts, and in other areas into conditions of permanent ice and snow. These climatic changes are best understood if we conceive that the earth once had a temperate to sub-tropical climate from pole to pole, a planetary temperature equilibrium, in short, a Greenhouse Effect.
Evolutionary-uniformitarians, geocentric rather than celestial in their views, tend to look downward for all changes, supposed to be gradual and slow. They fail to look upward for catastrophes, into the planetary realms, where evidence of past catastrophes sweep across the celestial scene. They exist literally from Mercury to Pluto, and do not exclude the asteroids, battered fragments of a former planet, or the Rings of Saturn, evidence of a second icy cataclysm in our solar system.6 Evolutionary-uniformitarians assume that the earth's North Pole could hardly have changed location within the last 5,000 to 7,000 years, merely because their framework of geocentric thought allows no room for such possibilities.
This article does not yield to such a non-catastrophic presumption. Indeed, if the flood was by nature tidal, it was indeed an astronomical catastrophe, likely of some five months duration. Such a celestial disaster necessarily would have wrought many effects on the earth system, including: (1) a change in the location of the earth's geographical poles; (2) a change in the tilt of the earth's axis; (3) a change in the eccentricity of the earth's orbit; (4) a change in the distance of the earth's orbit from the sun.
One may expand his mental horizon by considering celestial catastrophism side by side with a little catastrophic cosmology such as occurs in Job:
God, Which removeth the mountains, and they know not, Which overtaketh them in his anger, Which shaketh the earth out of her place, and the pillars thereof tremble, Which commandeth the sun, and it riseth not Which doeth great things past finding out, yea, wonders without number. Job 9: 5-10
Who can stay the bottles [planets] of heaven. Job 38:37b:
The vast subject of the past catastrophic interaction or engagement and disengagement of the earth with forces of astronomical dimension is further suggested in Job 38:32,33:
Canst thou bring forth Mazzaroth [a sort of wild card planet in the solar system] in his season? or canst thou guide Arcturus with his sons? Knowest thou the ordinances of heaven? canst thou set the dominion thereof in the earth?
Hence, while evolutionary-uniformitarians may make assumptions and suppositions of a serene astronomical past for the earth for any number of hypothetical millions of years, and while they may view the earth in isolation to its primary celestial environment, such assumptions must no longer be allowed to pass. The solar system, as a major environment, with a historic catastrophic potential from Mercury to Pluto and beyond, must be conceived within the catastrophic framework of thought.
Back to our planet, changes in weather are one matter, and sudden and permanent changes in climate are another. Humidity differentials are one factor within a climate. They are to be considered apart from (but concomitant with) temperature changes among other climatological factors. If there was a Greenhouse Effect embracing the planet Earth, then moderate, warm, subtropical temperatures and a constantly high relative humidity would have been a global phenomenon, of which more shall be considered later.
And God said, Let there be a firmament [atmosphere] in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters. And God made the firmament [the atmosphere], and divided the waters which were under the firmament [lakes, seas, swamps, oceans] from the waters which were above the firmament [the water vapor canopy], and it was so (Genesis 1:6-7).
Where wast thou when I laid the foundations of the earth? declare if thou hast understanding. Who hath laid the measures thereof, if thou knowest? or who hath stretched a line upon it? When I made the cloud the garment thereof, and thick darkness a swaddling band for it (Job 38:4, 5, 9).
Comment: The "swaddling band of the earth" is a term of translation describing this ancient condition, even as the Snohomish Indians called it a time when "the sky hung low." In the Genesis account the "firmament" suggests in English terra firma, but its meaning is quite different. It means "atmosphere." The waters below the firmament were the hydrography, the lakes, oceans, seas and swamps. The waters above the firmament comprised the canopy.
When he prepared the heavens, I was there: when he set a compass upon the face of the depth. When he established the clouds above: when he strengthened the fountains of the deep, (Proverbs 8:27-28).
Comment: In our current atmospheric arrangement, temperature declines as one ascends into the atmosphere, since pressure diminishes. The decline in temperature is termed the "adiabatic rate," and is between 3° and 3.5° per 1,000 feet. We suspect that the sea level surface temperature of much of the earth before the flood was between 60° and 70° F. At 10,000 feet in altitude, it was between 25° and 35° F. In 5,000 feet temperatures will drop about 15° to 18° F. It is proposed that the water vapor canopy was 3,000 to 5,000 feet thick, and ranged between 5,000 and 10,000 feet above sea level.
Some have proposed that the canopy must have been many miles thick, since there were forty days and nights of rain to condense out at the onset of the flood. This is a misunderstanding for several reasons. First, sunlight could not penetrate such a thick canopy. Secondly, if all of the current atmosphere were saturated at 1-½ percent to 3 percent concentration (with 15 pounds of pressure per square inch) this would comprise, or condense out, between 10 and 18 inches of rain per square inch of earth surface. This is not much of a flood. Thirdly, it has been suggested that an ice epoch dump, a catastrophic dump, occurred (a) simultaneously with the onset of the flood, and (b) over the magnetic, or auroral regions. The source of the rain was not atmospheric condensation primarily, but rather was low latitude slop-over of the ice dump. Ice particles provided the nuclei of condensation to sweep out the pre-flood canopy. Fourth, the source of water for the flood has also been demonstrated to be the oceans, surging in tidal formations, under conditions of earth deformation, the suggested "fountains of the deep" which surged for 150 days in the Genesis account. Hence, the proposal for a thick canopy is neither logical nor necessary.
And every plant of the field before it was in the earth, and every herb of the field before it grew, for the Lord God had not caused it to rain upon the earth, and there was not a man to till the ground. But there went up a mist from the earth, and watered the whole face of the ground — (Genesis 2:5, 6).
Comment: This observation states that there was (1) a total and universal absence of rain in the pre-flood world. It also directly suggests that there was (2) a daily or diurnal dew regime, based on humidity, saturation, temperature, dew-point, and condensation.
Both of these suggest a lack of planetary wind systems. For instance, dew will form only in the absence of wind. But more important, in today's climatic regime, whichever type of rain may fall, be it orographic, cyclonic, or convective, it is caused by one or more types of winds. Winds cause rain. But what causes winds? Temperature differentials across the earth's surface cause wind systems both on a local scale and on a global scale. Today the earth's atmosphere may be described as one vast wind machine, endeavoring to moderate the recurring temperature differentials across the latitudes and landforms.
For instance, today over the great continent Eurasia monsoons occur seasonally. This great continent heats up more rapidly than the surrounding oceans in the summer. Hot air rises and draws in cooler maritime air across the continental peripheries (edges). This cooler, maritime air happens to be humid, and it is termed the summer monsoon, with its warm, rain-bearing winds.
In the winter the reverse occurs. Cold, dead, heavy, polar air builds up over the frozen continent because the planet's crust gives off much heat, while receiving but little from the sun. These cold polar air masses become very heavy, build up and burst out of the center of Siberia. It is extremely cold and dry air. Thus, with a change in seasons and a change in the relative temperatures of land masses, the direction of the winds reverse. The quality of the winds sharply changes both in humidity and in temperature. This is a seasonal wind system.
However, let us discuss further the pre-flood Greenhouse Effect. The long wave radiation of the earth was captured and retained by (1) the low level water vapor canopy and by (2) a higher carbon dioxide mix throughout the atmosphere. With a Greenhouse Effect the low level canopy reflected much light and diffused the balance. The earth did not gain a great deal of heat during the daytime, nor did it lose much at night. A temperature equilibrium or near equilibrium was established.
Humidity naturally rose to near saturation or the saturation level. When night came, temperatures dropped 2 or 3 degrees. Dew-point was reached, and a thick layer of nocturnal dew was formed. During the day with an absence of dry, desiccating winds, evaporation was slow. The earth was well watered, both from the perspective of an abundance of condensation and a lethargy in evaporation. Swamps were abundant, but parched deserts of frigid tundras were not to be found in such a dew regime.7
Along with temperature, evaporation as well as precipitation is an essential to measure post-flood climates. For instance, today 10 inches of rainfall and/or snow is sufficient to grow a crop of wheat in a cool, brief summer of Saskatchewan, whereas 25 inches of rain may be quite insufficient in the hot, arid, parched climate of West Texas. The reason for the greater efficiency of the precipitation in Saskatchewan is the lower evaporation ratio. Before the flood, with (1) the canopy, (2) a nearly saturated atmosphere and (3) a temperature equilibrium, the evaporation rate was similarly very subdued. Hence, a rainless earth would be, and was, a well-watered environment (habitat).8
And they heard the voice of the Lord God walking in the garden in the cool of the day; and Adam and his wife hid themselves from the presence of the Lord God amongst the trees of the garden (Genesis 3:8).
Superficially, the "cool of the day" is a strange phrase in the pre-flood era of the Greenhouse Effect, with its reduced diurnal (daily) temperature range. With the coming of dusk and the dropping of temperature 2 to 3 degrees, the nearly saturated atmosphere again became saturated, as dew-point was reached. Condensation formed. A chilling layer of dew occurred. This, we suspect, was the "chill of the day" or the "cool of the day." This phrase does not refer to gross temperature decline, but, rather to dew-point and condensation.
In the six hundredth year of Noah's life, in the second month, the seventeenth day of the month, the same day were all the fountains of the great deep broken up, and the windows of heaven were opened (Genesis 7:11).
Comment: It has previously been noted how essential it is to understand the relationship between the flood, or tidal or gravitational phenomenon, and the ice dump, an electromagnetic phenomenon. Both were simultaneous. With the intrusion of ice particles through the magnetosphere and ionosphere into the lower troposphere, the ideal nuclei of condensation were suddenly provided. The canopy was cleaned out, and in a matter of hours. With its sudden departure came the sudden presentation of blue, blue sky. The windows of the atmospheric heavens appeared. The canopy was dissolved, or collapsed, the same day as the onset of the flood. The (blue) windows of heaven were opened.
The Scriptures suggest that the ark was already loaded with its human and animal cargo. Undoubtedly, the earth's crust was already shuddering and quaking from preliminary deformation. The same day of the flotation of the ark was the dissolution of the canopy, the seventh day of that chaotic period.
...and the windows of heaven were opened. And the rain was upon the earth 40 days and 40 nights. (Genesis 7:1lb-12) . . . 150 days later . . .(Genesis 7:24) And God remembered Noah and every living thing, and all the cattle that were with him in the ark, and God made a wind to pass over the earth, and the waters assuaged. (Genesis 8:1)
Comment: The establishment of the new, post-flood climate was based on a new atmospheric organization. The former low level water vapor in the troposphere had condensed out and vanished. In its stead were irregular, swirling cyclonic fronts of cloud systems frequenting certain latitudes and not frequenting other latitudes. A permanent heat disequilibrium of the planet's surface became the new norm. Direct sunlight shone across the latitudes and onto the crust at varying angles, heating the surface quite unequally.
(In addition, we deduce, a vast dump of ice on the two magnetic polar regions had been accomplished with 40 days of suddenness, and comprising ice well under -150° F., possibly under -200° F. This sudden ice dump covered some 20,000,000 square miles of area in each hemisphere. Massive ice flow and scouring commenced, surrounding and engulfing such mountains as the 5,000 foot Adirondacks. Mammoths became drowned and buried suddenly in sediments in some regions, and suddenly mummified in ice in the Siberian region. All of this ice and its subsequent melt added to the temperature disequilibriums both in the atmosphere and in the hydrosphere. Tropical marine crustaceans may continue to thrive in some places, but not in the Arctic Ocean.)9,10
It may be of more than passing interest to note something in the brief account in Genesis at the end of the flood, 8:1b, "And God made a wind to pass over the earth." A temperature disequilibrium, so absent from the pre-flood scene, is now so prominent, as are its resultant wind systems (cf. Job 38:29-30).
Temperature differentials, wind systems with the rain-bearing moistures, and/or their drying, desiccating effects were a part of the aftermath of the flood, as were outflowing ice masses. The fountains of the deep, the oceans, had ceased their surging. The 150 tragic, chaotic days of tides, rapid sedimentation, crustal deformation, massive ice dumps, and atmospheric reorganization were over - to say nothing of a probable polar relocation, a likely shift in axial tilt, and a likely orbital perturbation, with a new 91.5 and 94.5 million mile perihelion and aphelion orbit.11
Through all of this Noah remained something of a thirtieth century non-conformist – also something of a thirtieth century B.C. conservative. Two great tidal crescendoes had nearly destroyed the planet. He was not positive that everything was over. He remained in the ark another 210 days, just to be safe, and sent out some winged observers from time to time. Then he, his wife, his sons, and his daughters-in-law disembarked into the new era, a new and lonely, and, we are confident, a relatively windy world.
With the water vapor canopy gone, more short wave radiation, such as is in the ultra-violet range, bathed the earth's surface. Did this tend, or was it something else that tended to affect life in some mysterious way to shorten growth periods, and to shorten life spans? If so, how?
The Book of Genesis presents some rather astounding, extensive, and significant analysis on the ages of the patriarchs, both before and after the flood. This includes the "beget" and "begot" chapters of Genesis which may possibly bore a beginning reader. This theme will be discussed in greater detail later in this chapter and by Dr. McCone, in a later chapter. For the moment only the possibility of a change in atmosphere and a shortened life span for man is observed. Subtle or not in terms of atmospheric physics this is perhaps the most important - certainly one of the more important of all - of the changes between the pre-flood and the post-flood era, at least for man.
If the earth during the Greenhouse Effect era was so luxuriant and life-filled and bountiful, why? What was the pre-flood atmosphere like? How did the climatology work to effect gigantism in animals? How did the climatology work to effect a longevity for the human race? Why did men live for nine centuries before the flood? Partial answers may come from a more detailed analysis of the Greenhouse Effect.
Previously it was suggested that there was more water vapor and more carbon dioxide in the pre-flood atmosphere.
With a temperature equilibrium and a greenhouse effect, the normal tendency toward saturation by water vapor of the lower atmosphere proceeded unhindered by wind systems or rain. The troposphere of the earth contained perhaps three to five times as much total water vapor as does the current atmospheric envelope. Today barometric pressure at sea level is about 15 pounds per square inch. Before the flood it may have been within the range of 16 to l8 pounds, also producing a slight warming effect.
One may deduce there was more carbon dioxide in the pre-flood atmosphere for several reasons:
Thus, by three mechanisms, namely, by burial, by precipitation, and by dissolving in colder oceans, pre-flood carbon became locked out of the post-flood biosphere. The pre-flood atmosphere may have contained 0.2 to 0.1 percent carbon dioxide. Conservatively, we suggest it was at least over 0.1 percent. Table 1, page 19, recounts this estimate.
Concerning water vapor, it does not mix equally throughout the atmosphere due to lower temperatures in the stratosphere, where water vapor cannot be retained. Concerning carbon dioxide, however, it diffuses equally throughout the atmosphere and it is also particularly efficient at capturing long wave radiation. Whether the increase in carbon dioxide in the pre-flood atmosphere was more significant in the Greenhouse Effect than was the low level water vapor canopy is a moot point. The high carbon dioxide mix in the pre-flood atmosphere may well be the basic reason why the water vapor canopy did not burn off or dissipate.
Today in our upper atmosphere, the ionosphere, the intense cosmic rays from outer space enter into the earth's atmosphere and occasionally a particle will strike a nitrogen nucleus, causing a loss of an electron, which converts the nitrogen into heavy carbon, or carbon-14. This promptly reacts with oxygen to become carbon dioxide, but not of the regular C-12 variety.
When Libby presented the C-14 dating scheme, many of his assumptions and analyses were correct. For instance, he assumed that the half life of C-14 was 5600 years, which was close enough. Its presence in a non-renewable state in dead organic material did provide a clear potential and a new horizon for dating schemes.
Libby made nine assumptions in his dating scheme - five of which seem to us to be correct. But, unfortunately, Libby subconsciously made some uniformitarian assumptions which merit scrutiny and rejection. Libby assumed a constancy in the earth system during the last 100,000 years, a subconscious uniformitarianism, for the following:
It must be added that C-14 dating has been tested on artifacts of known historical dates, and the margin of error climbs to significant proportions for materials older than 2,500 years, or materials older than 500 B.C. Dr. Chittick, author of the next article, holds that when the aforementioned assumptions 1, 2, and 3 of Libby, regarding uniformitarian earth history, are exchanged or substituted out in favor of catastrophic assumptions regarding the flood, the chronicles of Genesis harmonize and merge with a Revised Catastrophic C-14 Dating Schedule.
Ice dumps three miles deep over the North Magnetic Pole ... ice dumps 5,000 feet below sea level in Antarctica ... quick frozen mammoths ... ice and lava formations interleaved or sandwiched together ... radial ice flow patterns ... volcanic ash intermixed with ice 5,000 feet below sea level - all of these are facts. Yet, nowhere within popular (uniformitarian) geology has a comprehensible explanation been tendered. But then, popularity does come and go. Perhaps uniformitarianism will, too.
We propose that in the placid, non-circulating pre-flood atmosphere a buildup of C-14 occurred which suddenly mixed with flora and fauna in abnormal proportions. The implication of just this variable in atmospheric mix must be reassessed in order to come up with a realistic dating schedule.
C-14 is a product of the upper atmosphere where the withering, direct, unshielded rays of the sun interact with the outer atmosphere. This is the same region where, on Venus, short wave radiation produces the abnormal high level canopy of carbon suboxide. Are there any other significant developments in the upper atmosphere of the earth which, possibly subtly, possibly profoundly, affect the atmosphere? We think so.
Like C-14 and carbon suboxide, ozone is manufactured in upper atmospheres. Where carbon dioxide is abundant, as in Venus's atmosphere, carbon suboxide is the product. Where Oxygen is abundant, as in the Earth's atmosphere, ozone in dilute proportions is formed. Ozone is created when an oxygen molecule (O2) is split by short wave radiation. The individual Oxygen atoms recombine into an abnormal form of oxygen, ozone (O3). Chemically, C-14 reacts just like the normal C-12. Chemically, ozone does not react just like the normal oxygen molecule.
In the twentieth century atmospheric environment ozone exists in the upper atmosphere in levels of about one to three parts per million.
Ozone is not distributed uniformly through the atmosphere, but is mostly concentrated between 10 and 40 km above the earth's surface, with a fairly sharp peak in distribution at about 20-30 km.14
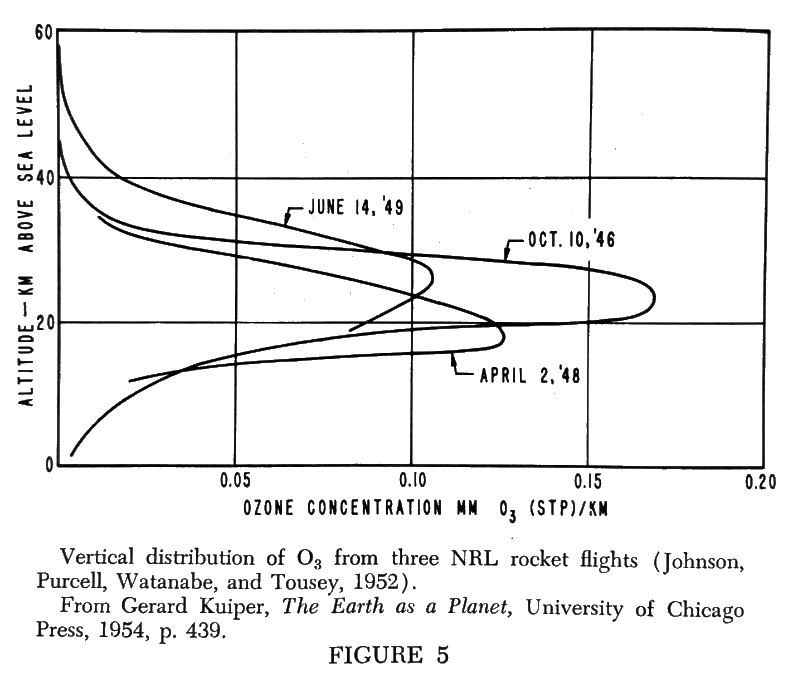
Ozone is manufactured by short wave radiation in the upper atmosphere. But one might ask, "How does it decay or decrease?" Does it constantly increase or build up? The answer is no. Whereas, it is manufactured by short wave radiation, it is similarly reconverted or catalyzed back into the normal oxygen (O2) by long wave radiation, such as the sun provides, and particularly such as the earth's crust gives off. The reconversion of ozone back into oxygen is achieved with increasing efficiency as ozone circulates, or fluxes, downward toward the crust. At sea level today it will vary from one to three parts per 100,000,000, varying somewhat with prevailing winds, magnetic storms, and closeness to high magnetic latitudes. What effect could such a dilute gas as a few parts per million have upon the earth's outer atmosphere?
The ozone layer is thus a buffer between the continuance of terrestrial life as we know it at present and sudden extinction by the short wave rays of the Sun, against which we have no physiological protection,15
Sunlight, unfiltered by ozone, is rich in the potent ultraviolet rays which rupture chemical bonds in protoplasm and thereby destroy life. Life exists on earth now only because we are shielded from direct ultraviolet rays by a dilute but extremely essential high level blanket of ozone which our atmosphere provides.16
Hence, we may realistically hold that in today's atmosphere the Earth does possess a canopy, though unseen by the human eye (which sees only wave lengths between 3,000 and 8,000 Å ). Today we have a very thin canopy, a very high one, but a very crucial one.
Now let us consider the low level water vapor canopy of Figures 1,2, 3, and 4. The low level water vapor canopy efficiently captured long wave radiation, which otherwise would convert ozone back to oxygen. An increased abundance of carbon dioxide would do the same thing. Hence, in a Greenhouse Effect structure of the atmosphere, a considerable amount of long wave radiation was filtered out in the lower atmosphere, allowing for a lower reconversion rate of ozone to oxygen. This in turn would result in a thicker high level ozone canopy - one in which no wind systems brought dilute amounts to the surface. We propose that the pre-flood ozone canopy was (a) thicker in the upper atmosphere by a considerable amount, and more concentrated, and was also (b) slightly higher in elevation due to a greater barometric pressure in the pre-flood era.
Ozone in our atmosphere, the atmosphere you and I breathe, contains a few parts of ozone per hundred million. This is increased in metropolitan areas. It is increased in stratocruisers [commercial jets] or submarines and in some manufacturing environments. It is increased in or near x-ray laboratories, or arc-welding locations, or cyclotrons. What could a few parts per hundred million of ozone do to the human physiology?
Perhaps this could be better answered by asking what a few parts per million does to human, or animal physiologies. Ozone is an unstable, corrosive, and highly reactive gas, bluish in color in thick layers. Ozone has been measured as high as 11 ppm in the stratosphere, from which there is a steady downward flux due to wind systems into the troposphere, where it is destroyed by catalytic reactions, chemical and photochemical reactions. Its effects on a number of plant species, as an oxidant, is singly harmful. At 0.05 to 0.1 ppm its odor becomes pronounced.
A study of 11 subjects exposed to 0.6 to 0.8 ppm ozone for one two-hour exposure resulted in a significant reduction in lung diffusing capacity. After-effects involved bronchial irritation and soreness, and a slight dry cough lasting 12 to 24 hours. At a higher concentration of 1.5 to 2.0 ppm, also for a single two-hour exposure, the result was general morbidity lasting two weeks, accompanied by impaired lung function, chest pain, coughing and extreme fatigue.
When humans breathed in 1 ppm ozone for 10 minutes, a decrease in oxygen consumption occurred, plus the sphering of red blood cells. Other findings indicate that ozone may produce secondary effects on body metabolism, damage to myocardial tissue, lung adenomas and general aging effects.
Ozone has been found to be lethal to laboratory animals in concentrations of 3.6 to 20 ppm within several hours. Ozone in lesser concentrations is found to be closely related to increasing mortality rates for laboratory animals.17
Increased aging effects of ozone in concentration of parts per ten million are interesting. It is also of interest to note that radiologists, physicians, who often avoid x-ray technician operations, yet work in a slightly over-ozonated atmosphere, have life spans 7 years shorter than the average among all physicians.18
Robert Fettner, experimenting in England with fish exposed to water ozonated eight parts per million, ozone in oxygen, found that fish, living in said ozonated water, experience a sharp decline in longevity, a decline which can be described by a transient decay curve. He further concluded:
This investigation has demonstrated that exposure to ozone is capable of producing chromatid breakages in human cell cultures, which are apparently identical to those produced by x-rays.19
The decline of the life spans or the decline of longevity in man after the flood is also described by a transient decay curve whether by coincidence or not, as is illustrated in Figure 6.
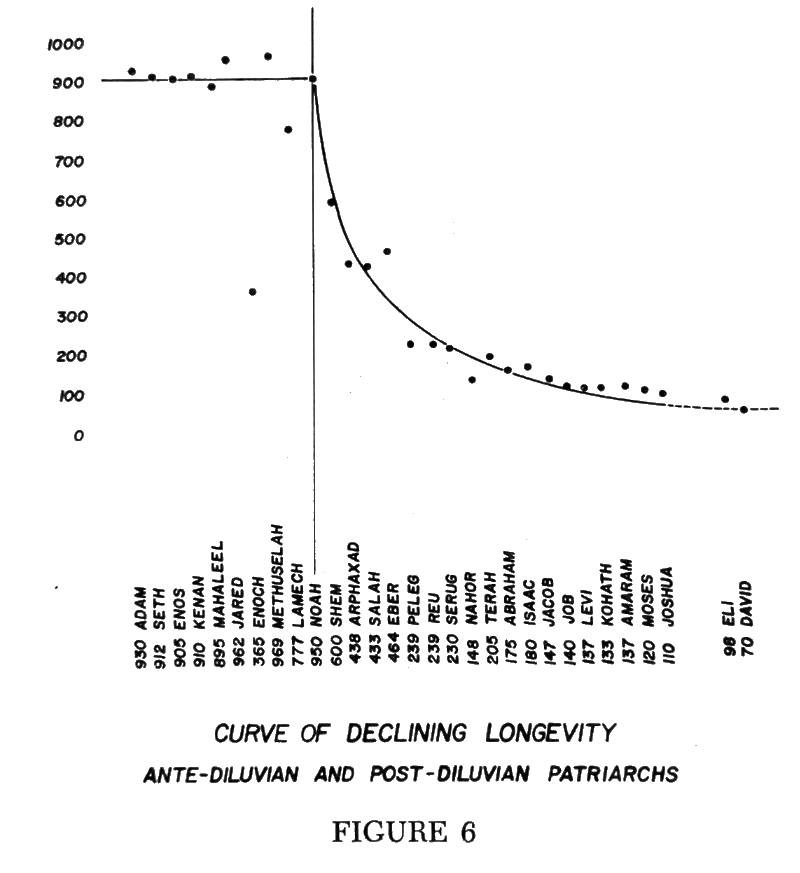
In the pre-flood world there was either no ozone at the surface of the earth, where man and animals breathe, or else it existed in dilutions of parts per trillion, as contrasted with the current atmosphere, where toxic, corrosive ozone exists in parts per hundred million naturally, and higher in some industrialized environments.
The pre-flood world had the better of both ozone potentials.
Hence, the fauna (animals) had the best of both possibilities (a better high level ozone shield and a non-ozonated lower atmosphere). Similarly, plants had the better of both potentials, having more water and (in a dew regime) more carbon dioxide both available. We are not suggesting that barley grew nine inches in seven days in the pre-flood world, as has ben achieved under experimental conditions. But we do propose that vegetation flourished more than today, and on a pole-to-pole basis.
We further propose that in the pre-flood atmosphere, not only did animals tend to grow larger - we propose that they matured more slowly, and aged much more slowly. Today the average person may inhale ten million times per year, and may inhale the equivalent of one third of a breath of pure ozone. It is proposed that in the pre-flood atmosphere man would not inhale a tenth of a pure breath of ozone in a thousand years, or should we say, in the Methuselaic 969 years.
If mankind lived in an atmosphere of several parts per 10,000 cyanogen or mustard gas, he would display much concern. Research into the physiological effects of ozone is mostly a phenomenon of the last five years. Mankind does live in a mildly corrosive, poisoned, or ozonated atmosphere, and yet is hardly aware of its significance, partly because of the extreme dilution.
Adam and Methuselah lived in a non-ozonated atmosphere. They lived in an era when lizards forgot to quit growing, and dinosaurs abounded. Insects developed 20- and 30-inch wing spans. Birds developed 15- and 25-foot wing spans. Large fish existed. Five-foot frogs and 12-foot turtles were normal. Sloths of 10,000 pounds existed. Mammoths were twice as large in terms of weight as are modern pachyderms. This same principle runs throughout the mammalian world, be it canines and saber-toothed mesonyxes (about as large as Great Danes), be it felines such as saber-toothed panthers and tigers, be it mammoths whose tusks sometimes arched in 300° of (an almost) complete circle, or be it man who may have been nine feet tall and 900 years old. "And there were giants in the earth in those days" (Genesis 6:4a).
It may be of interest to mathematicians to discover that after the flood catastrophe one might double the number of generations from Noah, and he can pretty much half the life span. This proceeded down to approximately 1,000 B.C. where the curve finally leveled out at threescore and ten. We suspect that the effects of an ozonated atmosphere, reinforced by a higher level of ultra-violet radiation, produced cumulative effects within the human race. Since the first six generations all died about the same time, could this indicate that the germ tissue, the gametes, were physiologically brought into a new and harsher physical environment?
We further suspect that, with mankind, he became increasingly alarmed when Arphaxad lived 438 years, whereas, great-grandson Peleg lived only 239. Peleg's great-grandson, Nahor, lived but 148. What was happening? How concerned and dismayed must have been those sixth and eighth generation post-diluvians. We suspect here is the basis for the cult of the dead motif, the death psychosis, which so deeply pervaded ancient Egyptian culture where the death of the head of a family became a super-tragic event, and death-journeys up the Nile to mummified entombment became national spectaculars. This is part of ancient thoughts and values.
But evolutionary-uniformitarianism tells us that man has changed for the better and we have little of importance to learn from the past. For creationists and catastrophists, however, this article is an opening wedge into the consideration of the Greenhouse Effect, and paleoclimatology, one part of the far larger subject of the flood-ice catastrophe. This article is a beginning probe, hopefully, to more thorough and comprehensive investigations of the past. Perhaps it is a spur to investigate what would occur in laboratory conditions to animals subjected, not to super-ozonated conditions as in the works of Fettner and Jaffe, et al, but rather to completely non-ozonated conditions. Would longevity again become, to some degree, re-established? Would a prevailing gigantism among animals again recur? We suspect so.
The following conclusions are made concerning the Greenhouse Effect, and its component, the pre-flood canopy in the troposphere:
Smith, A. E. Wilder, Man's Origin, Man's Destiny, Wheaton, Ill., Harold Smith Publishers, 1968, pp. 96-97, 136-137. Items are credited to geologist Clifford L. Burdick. ↩︎
These fossil human footprint impressions are side by side with dinosaur footprint impressions. Man appeared on the scene a mere 1,000,000 evolutionary years ago, whereas, dinosaurs presumably disappeared from the scene about 60,000,000 evolutionary orbits ago. Evolutionary mythology doesn't regard the two as being within 59,000,000 years of each other, much less simultaneous. ↩︎
Hooker, Dolph E., Those Astounding Ice Ages, New York; Exposition Press, 1948, p. 44. ↩︎
Loc. cit. ↩︎
Charles Hapgood, "The Mystery of the Frozen Mammoths," Coronet, Sept. 1960, p. 74. ↩︎
Patten, Donald W., The Biblical Flood and the Ice Epoch, Seattle, Washington, Pacific Meridian Publishing Co., 1966, pp. 27-50, 137-193, 277-308. ↩︎
It may be of interest to the reader to note another type of artificial Greenhouse Effect, under experimental research by the Kwick-Lok Industries, Inc., of Yakima, Washington. Here barley seeds are experimentally laid out in pans in a type of large enclosed walk-in freezer type container. There are four small fluorescent tubes, one in each corner. The trays of barley seed are kept under conditions of saturation and warm constant temperature. They are sprayed with water and nutrients six times daily. Under these conditions barley is seen to grow 9 to 11 inches high in 7 days, without sunlight and without soil. This can theoretically be done in Alaska as easily as in California. This is an artificial Greenhouse Effect, bearing a few resemblances to the pre-flood world, where diurnal condensation and a permanent cloud cover pervaded. ↩︎
Patten, Donald W., op. cit., pp. 63-64. ↩︎
Morris, Henry M., et al, A Symposium on Creation (I), Grand Rapids, Michigan, Baker Book House, 1968, p. 119-135 ↩︎
Patten, Donald W., op. cit., pp. 101-136. ↩︎
Patten, Donald W., Evangelical Flood Cosmologies, Seattle, Washington, Pacific Meridian Publishing Co., 1968, pp. 27-31. ↩︎
Patten, Donald W., op. cit., p. 101-136, 277-280. ↩︎
Cook, Melvin A., "Radiological Dating and Some Pertinent Applications of Historical Interest, Do Radiological 'Clocks' Need Repair," Creation Research Society Quarterly, Vol. 5, No. 2, Sept. 1968, p. 69. ↩︎
Kuiper, Gerard P., The Earth as a Planet, Chicago, University of Chicago Press, 1954, p. 439. ↩︎
Smart, W. N., The Origin of the Earth, Baltimore, Penguin Books, 1959, p. 56. ↩︎
Howe, George F. Unpublished Paper. Creationistic Botany Today: A Progress Report, 1969, 24635 Apple St., Newhall, Calif. It is anticipated that this paper will be published in Symposium on Creation III, scheduled for release in early 1971. ↩︎
Jaffe, Louis S., "The Biological Effects of Ozone on Man and Animals," American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, May-June, 1967,pp. 267-276. ↩︎
The number of molecules per cubic centimeter is 2.69 x 1019, Minimum concentrations of ozone in the free atmosphere are 1 part per 100,000,000, and are somewhat higher naturally, and much higher in some industrialized areas. For instance symptoms of ozone toxicity are common in stratocruisers, submarines, and around arc welding areas. Ozone is a factor in industrial smog. This means that in the atmosphere which we currently breathe, there are a minimum of 2.69 x 1011 molecules of ozone per cubic centimeter, even at this dilution. Again, we contend that in the pre-flood atmosphere, the concentration of molecules of ozone per cubic centimeter was virtually nil. ↩︎
Fettner, Robert, Nature, London; May 1962, Vol. 194, p. 793. ↩︎
Wilson, Talmage, frontpiece, as quoted in Patten, Donald W., The Biblical Flood and the Ice Epoch, op. cit. ↩︎
For further information or to contact Baker Books regarding their other fine publications, click below:
Go to "A Symposium on Creation" Vols. 1-6 Go to Main Page of: www.creationism.org